Understanding High Blood Pressure: A Clear Explanation
To grasp the concept of high blood pressure, it’s essential to understand what blood pressure itself is.
What Is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is the force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of our blood vessels, particularly the arteries. Our circulatory system is an intricate network of these vessels that deliver oxygen and nutrients to every cell in the body.
Arteries, the vessels that carry blood away from the heart, are made up of muscle and elastic tissue, allowing them to withstand the pressure of the blood being pumped through them. This is much like water flowing through a garden hose, which creates a certain amount of pressure within the hose.
The blood pressure results from two forces: one created when the heart pumps blood into the arteries and another when the heart is at rest between beats. These forces are crucial for maintaining proper blood flow throughout the body.
The Significance of Blood Pressure Readings
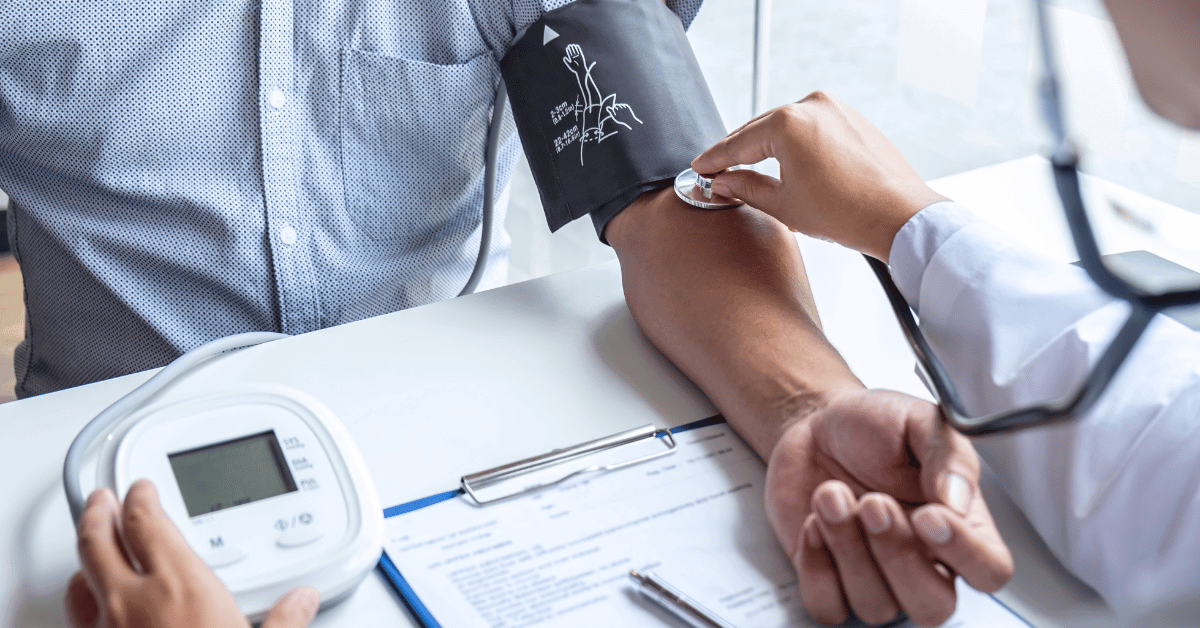
A typical blood pressure reading includes two numbers, often expressed as one number over another, for instance, 120 over 80. The first number is known as the systolic blood pressure, which measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats. The second number, the diastolic blood pressure, records the pressure when the heart rests between beats.
These readings indicate how much pressure your blood exerts against your artery walls, both when the heart is actively pumping and when it is relaxed. Understanding these numbers is critical in monitoring and managing blood pressure.
For the general population, an average blood pressure is considered to be around 120/80 mmHg. However, interpretations of what is considered ‘normal’ or ‘high’ can vary by country. In some places, an upper limit of normal might be considered as high as 140/90 mmHg, which some health professionals feel is quite elevated, particularly for younger individuals.
The Universal Importance of Blood Pressure Checks
Regardless of the reason for a patient’s visit to a clinic, it’s a common practice for healthcare professionals to conduct a blood pressure check as part of a general health assessment. Such check-ups, known as Wellman or Wellwoman check-ups, are crucial for the early detection and management of high blood pressure.
Even if individuals visit the clinic for unrelated concerns, measuring their blood pressure can reveal underlying cardiovascular risks. Everyone must understand the importance of regular blood pressure monitoring to maintain overall health and wellness.
Hypertension management is a crucial aspect of preventative healthcare, and understanding one’s blood pressure readings is the first step towards taking control of one’s cardiovascular health. Through education and awareness, individuals can work with healthcare professionals to ensure their blood pressure remains healthy, reducing the risk of severe health complications.
Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
While high blood pressure often goes unnoticed, certain symptoms can hint at its presence. One common indicator is persistent headaches. Rather than simply mitigating the discomfort with over-the-counter painkillers, it’s important to consider that a headache could be a symptom of elevated blood pressure. Similarly, visual disturbances might hint at hypertension and warrant a blood pressure check.
Other physical signs to be aware of include:
- Feelings of fatigue or confusion
- Severe chest pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Irregular heartbeat
- Blood in the urine
Consulting one of our healthcare providers is strongly advised if these symptoms are observed, especially in combination or frequently.
The Relationship Between Stress & High Blood Pressure
Stress is a natural aspect of life, but its chronic presence can adversely affect blood pressure. When stressed, the body releases hormones like adrenaline and noradrenaline, which lead to vasoconstriction—the narrowing of the blood vessels. This physiological response increases blood pressure because the heart has to pump harder to circulate blood through these constricted vessels.
Strategies to Manage Stress & Maintain Healthy Blood Pressure
To combat the effects of stress on blood pressure, consider employing techniques such as:
- Regular exercise: Physical activity helps lower blood pressure by keeping the heart and blood vessels in optimal condition.
- Mindfulness and meditation: These practices can decrease stress hormones and promote relaxation, which is beneficial for blood pressure.
- Adequate sleep: Lack of sleep can elevate stress and, in turn, blood pressure. Maintaining a regular, restful sleep pattern is important.
Addressing stress is a key component of blood pressure management, and implementing these strategies can help maintain a stable blood pressure reading.
The Consequences
Leaving high blood pressure untreated can have serious repercussions. One of the potential dangers is damage to the blood vessels of the eye, leading to bleeding in the sclera. This is an example of how hypertension can manifest in visible physical symptoms.
The heart, a muscle that tirelessly pumps blood, is particularly vulnerable to the persistent strain caused by high blood pressure. Over time, a heart that is continuously working against increased resistance can grow weaker, leading to conditions like heart failure or an enlarged heart.
Preventative Measures & Regular Monitoring
To forestall such dire outcomes, proactive measures must be taken to manage blood pressure:
- Consistent monitoring of blood pressure, especially in individuals with a family history of hypertension
- Dietary changes, such as reducing salt intake and eating more fruits and vegetables
- Limiting alcohol and caffeine consumption
- Stopping smoking, which can acutely increase blood pressure and cause long-term damage to blood vessel walls
In addition to lifestyle changes, medication may be prescribed to help control blood pressure. It is crucial to follow a healthcare professional’s guidance and regularly evaluate and adjust treatment plans.
Maintaining awareness of the risks and symptoms of high blood pressure, managing stress effectively, and adopting a healthy lifestyle are all vital components in preventing and controlling hypertension. With vigilant care and attention to one’s body and habits, the risks associated with high blood pressure can be substantially mitigated.
The Importance of Sodium Regulation
Excess sodium intake is an often underestimated risk factor in developing high blood pressure. Sodium, commonly consumed as salt (sodium chloride), significantly impacts blood volume and pressure in the arteries. Though the body requires some sodium to function properly, too much prompts it to retain water, which raises blood pressure.
Reducing Sodium Intake
Here are some practical ways to reduce sodium consumption:
- Read labels: Pay attention to the sodium content in packaged foods, which can be surprisingly high.
- Taste before seasoning: As suggested by health experts, one should taste food before automatically adding extra salt.
- Use herbs and spices: Enhancing food flavours with various herbs and spices can reduce the need for salt.
- Cook from scratch: Preparing meals at home allows full control over the amount of sodium used.
By taking these measures, individuals can protect their cardiovascular health and prevent the risk of hypertension.
The Impact of Alcohol
Regular consumption of alcohol can lead to a rise in blood pressure. While moderate drinking may have some health benefits, excessive alcohol use is a well-established risk factor for hypertension.
Guidelines for Alcohol Consumption
To avoid alcohol’s negative effects on blood pressure:
- Adhere to recommended drinking limits, keeping moderation in mind.
- Consider alcohol-free days to reduce overall weekly intake.
- Opt for lower-alcohol alternatives when possible.
These steps can help prevent alcohol-induced increases in blood pressure and contribute to overall health and well-being.
Weight Management
Obesity is a known contributor to high blood pressure. It’s not solely the presence of excess weight that poses a risk but also the location of the fat deposits. Visceral fat, which is stored around the organs, can be particularly harmful as it may constrict blood vessels and force the heart to work harder.
Strategies for Healthy Weight Maintenance
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is beneficial for controlling blood pressure:
- Regular physical activity: Emphasize exercise you enjoy to ensure it becomes a sustainable part of your routine.
- Balanced diet: A diet rich in whole foods, such as lean proteins, whole grains, and fruits and vegetables, helps manage weight.
- Monitor portion sizes: Being mindful of portions helps prevent overeating, even with healthier food choices.
Maintaining a healthy weight through these strategies not only aids in managing blood pressure but also supports overall health.
Acting on Blood Pressure Symptoms
If headaches, tiredness, or a throbbing sensation in the head are experienced, taking these symptoms seriously is crucial, as they may indicate high blood pressure.
Responding to Hypertension Symptoms
Consider the following actions if experiencing potential hypertension symptoms:
- Schedule a medical evaluation: Discuss any concerning symptoms with your healthcare provider.
- Monitor your blood pressure: Regular self-monitoring can help detect hypertension early.
- Adjust lifestyle habits: Implement changes based on the guidance regarding diet, alcohol consumption, exercise, and weight management.
Awareness and proactive management of risk factors play vital roles in preventing and treating high blood pressure. Regular check-ups and a commitment to a healthy lifestyle are fundamental to reducing the risk of hypertension-linked complications such as heart failure and stroke. Individuals can significantly influence their blood pressure and health outcomes through educated efforts and sustained health-promoting practices.
Self-monitoring & Early Detection
Recognizing the early symptoms of high blood pressure, such as feelings of heat and flushing without an apparent trigger, is essential for prompt and proactive health management. High blood pressure typically presents few noticeable symptoms, so individuals must be attentive to subtle body changes.
Proactive Monitoring at Home
Acquiring a basic blood pressure monitor available from pharmacies or online retailers like Amazon allows for regular home assessments. Periodic self-checks are valuable for:
- Detecting changes early: Recognizing blood pressure elevations before developing severe symptoms could prevent further health complications.
- Tracking blood pressure trends: Understanding personal blood pressure patterns aids in identifying the effects of lifestyle adjustments or medication.
When to Seek Professional Health Advice
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional in case of persistent symptoms. They will:
- Evaluate the symptoms and check for possible health issues, including high blood pressure.
- Provide guidance on preventing the progression of hypertension.
- Offer tailored advice on risk reduction and maintenance strategies.
Prevention Over Cure
Embracing a preventative approach to health can mitigate the risk of severe hypertension and its associated health dangers. Installing a ‘fence’ before a ‘fall’ metaphorically illustrates the importance of protecting health through foresight and action.
Key Preventative Strategies
To avoid the detrimental effects of uncontrolled blood pressure, consider these preventative measures:
- Regular medical screenings: Routine check-ups can catch blood pressure issues before they escalate.
- Lifestyle modification education: Learning about healthy behaviours can stave off the development of hypertension.
- Community health initiatives: Participating in local health programs can offer support and resources for managing blood pressure.
By prioritizing prevention, individuals can significantly decrease the likelihood of enduring the ‘broken bones’ associated with the metaphorical fall of hypertension-related health crises.








It’s insane how something as seemingly small as a headache can signal something as serious as high blood pressure. Our bodies have some wild ways of letting us know when something’s up.